Call: 07971460098
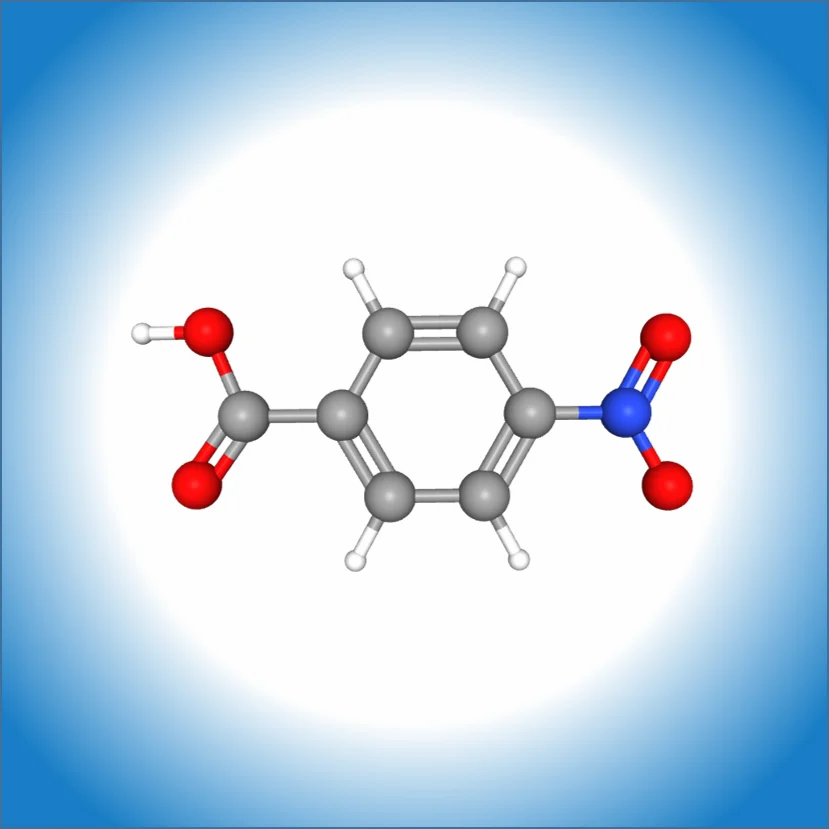
PARA NITRO BENZOIC ACID
PARA NITRO BENZOIC ACID Trade Information
- Payment Terms
- Cash in Advance (CID)
- Delivery Time
- 7 Days
- Main Domestic Market
- All India
About PARA NITRO BENZOIC ACID
p-Nitrobenzoic acid (4-nitrobenzoic acid) is a pale yellow organic solid used as a chemical intermediate in synthesizing products like dyes, pigments, pharmaceuticals (such as the anesthetic procaine), and in wastewater treatment. It is a stronger acid than benzoic acid due to the electron-withdrawing effect of the nitro group, and it has a melting point around .
Properties and uses
- Appearance: Pale yellow crystalline solid.
- Melting point: .
- Solubility: Soluble in water and oxygenated/chlorinated solvents.
- Acidity: A stronger acid than benzoic acid.
- Uses:
- Intermediate for dyes and pigments: Used in the production of azo dyes, pigments, and colorants for textiles, plastics, and inks.
- Pharmaceutical precursor: A precursor to procaine and other pharmaceuticals.
- Wastewater treatment: Used to remove protocatechuic acid from wastewater.
- Biosynthesis: Participates in the biosynthesis of the antibiotic aureothin.
Synthesis
- It can be prepared by oxidizing p-nitrotoluene with oxidizing agents like nitric acid, chromic acid, or permanganates.
- Another method is reacting sodium nitrite with p-hydroxybenzoic acid.
Safety
- According to Tokyo Chemical Industry, it is harmful if swallowed, may damage fertility or the unborn child, and may cause damage to organs.
- Always use proper handling procedures and personal protective equipment when working with this chemical.


Tell us about your requirement

Price:
Quantity
Select Unit
- 50
- 100
- 200
- 250
- 500
- 1000+
Additional detail
Mobile number
Email
More Products in Api Intermediates Category
4 Methoxybenzoic Acid
Price 650 INR / Kilograms
Minimum Order Quantity : 1 Kilograms
Color : Multiple
Purity(%) : 98 %
Storage : Dry Place
Usage : Industrial
3-Carbamoymethyl-5-Methylhexanoic Acid
Price 800 INR / Kilograms
Minimum Order Quantity : 1 Kilograms
Color : Multiple
Purity(%) : 98 %
Storage : Dry Place
Usage : Industrial
4 Amino 6 Chloro 1 3 Benzene Disulfonamide
Price 1050 INR / Piece
Minimum Order Quantity : 1 Piece
Color : Multiple
Purity(%) : 98 %
Storage : Dry Place
Usage : Indusrial
4 Hydroxyacetophenone
Price 650 INR / Kilograms
Minimum Order Quantity : 1 Kilograms
Color : Multiple
Purity(%) : 98 %
Usage : Industrial

 Send Inquiry
Send Inquiry Send Inquiry
Send Inquiry




 English
English Spanish
Spanish French
French German
German Italian
Italian Chinese (Simplified)
Chinese (Simplified) Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Arabic
Arabic Portuguese
Portuguese